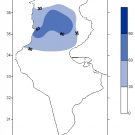
Air quality improved significantly during the confinement, which has now lasted almost a month and a half (March and April). A spectacular fall in nitrogen dioxide (NO2), Sulfur dioxide (SO2) and Carbon Monoxide (CO) produced mainly by human activities, was observed during this period in several Tunisian cities and in particular in the North and at the Center, using satellite measurements from the European center by the European Earth monitoring program - COPERNICUS -, analyzed and developed at the National Institute of Meteorology (INM).